On this page
Area Light is a material type that will give you a wide range of light dispersion. This will function similarly to a flood light.

Color
Here, you can choose the color the light will cast. You can also place a texture in front of the light source to color and mask the emitted light.
For accurate lighting colors, use the Kelvin scale to select accurate lighting temperatures.




Power
The power of the light can be controlled in either Watt, Lumen or Lux. Lumen or Lux are recommended for best results. The choice between Lumen or Lux depends on the preferred workflow.
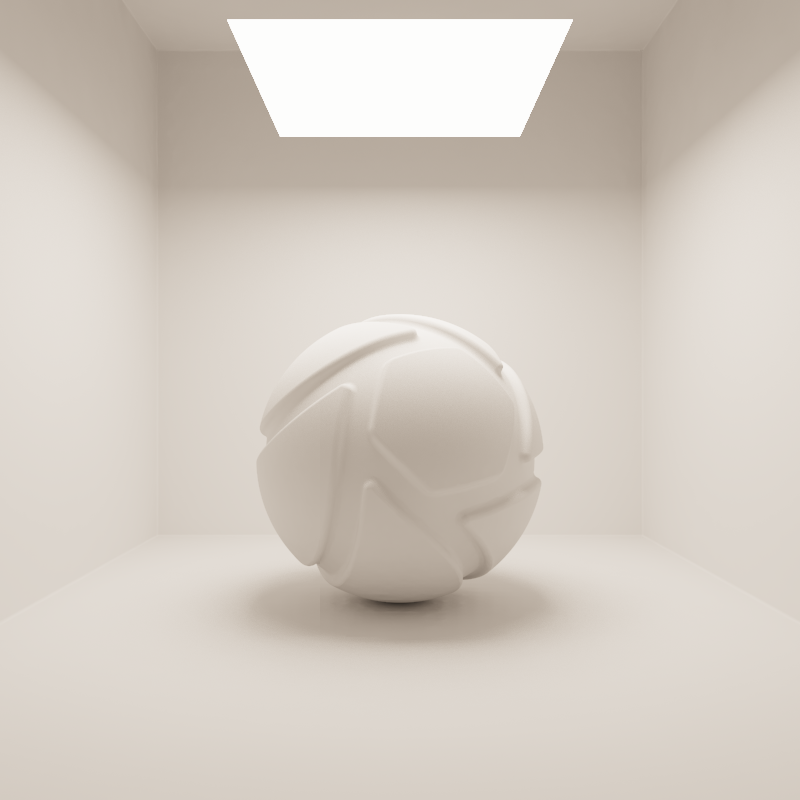
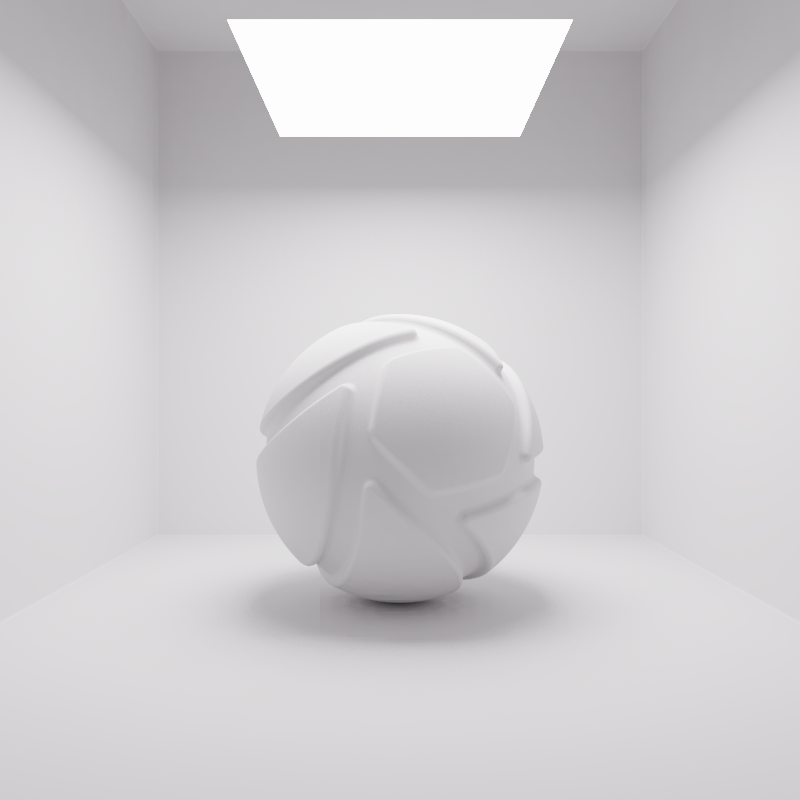
Lumen
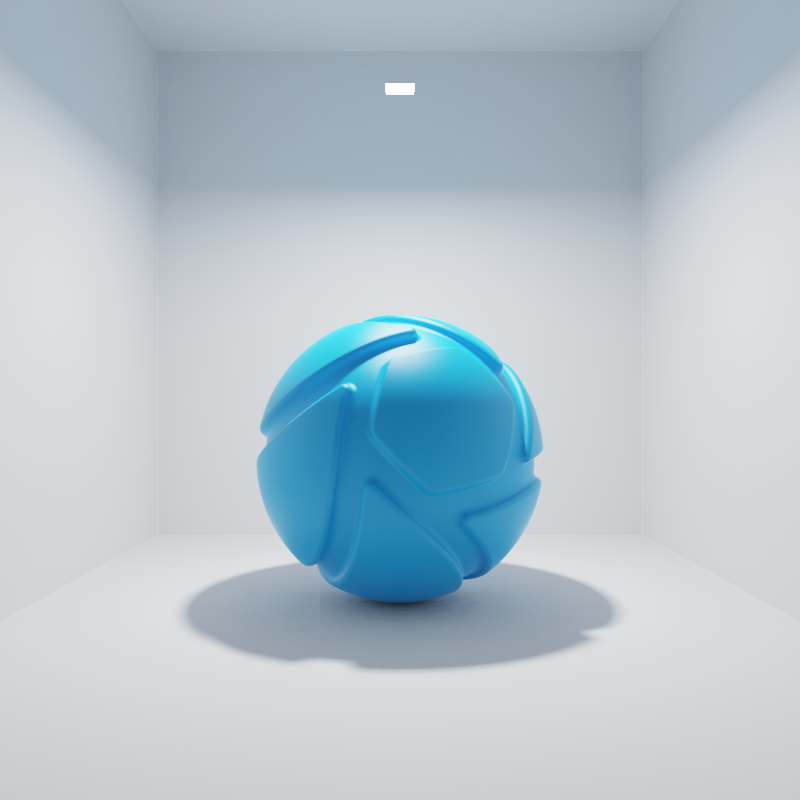
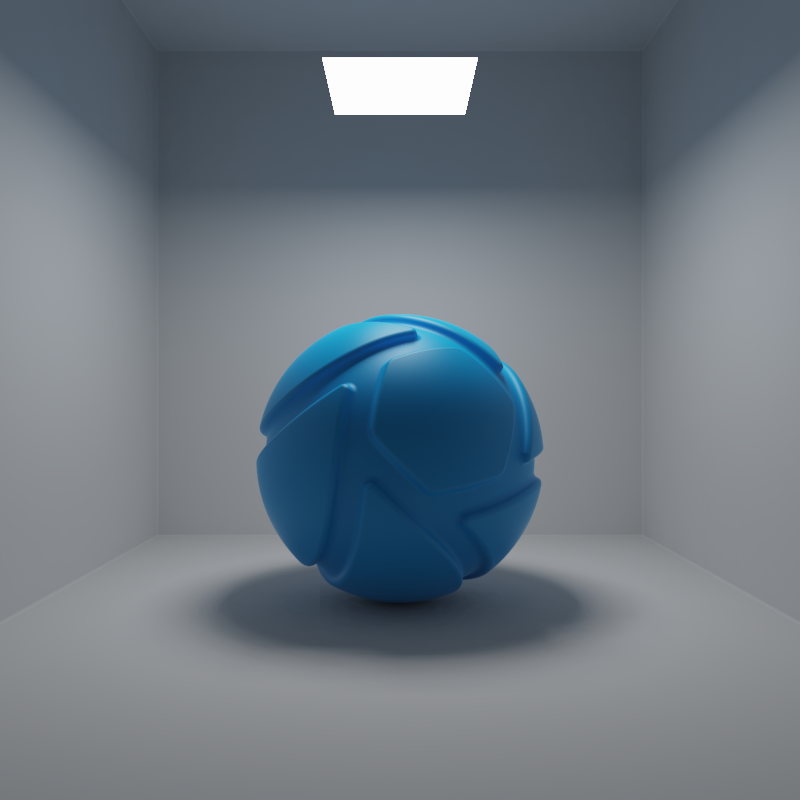
When the Power unit is set to Lumen, then the light output is specified as luminous flux. Total light output will be constant for area light objects of different sizes.
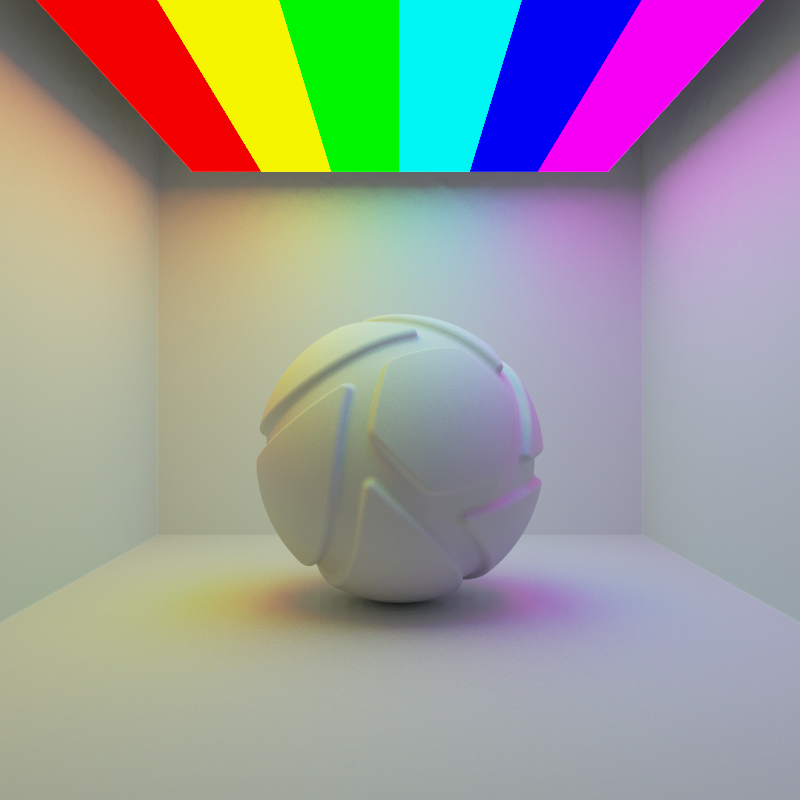
The examples below show the effect of increasing the size of a square area light from 10 to 200 mm. Power is a constant 250 Lumen.
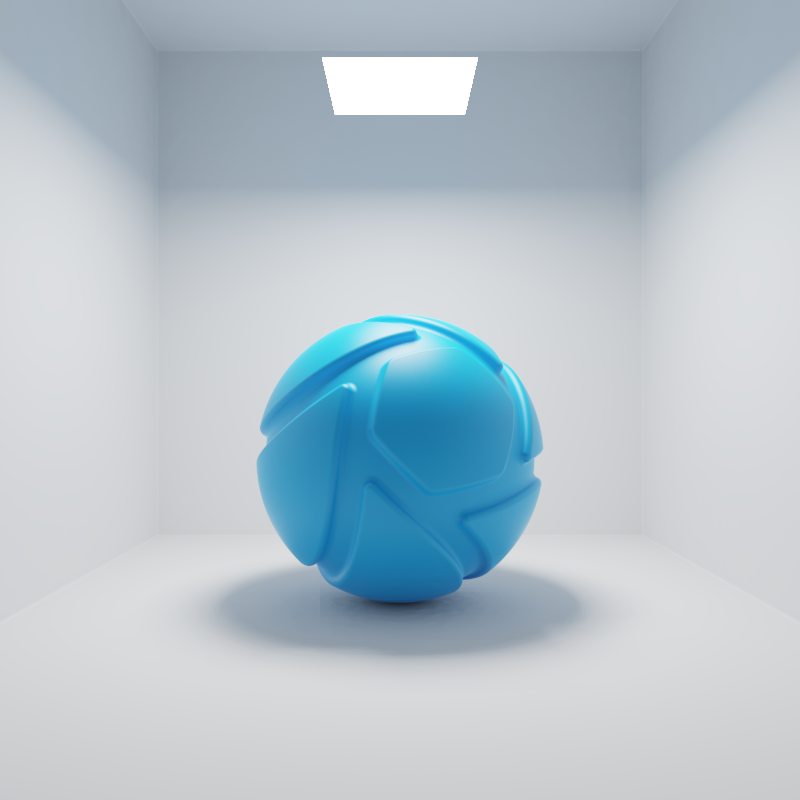
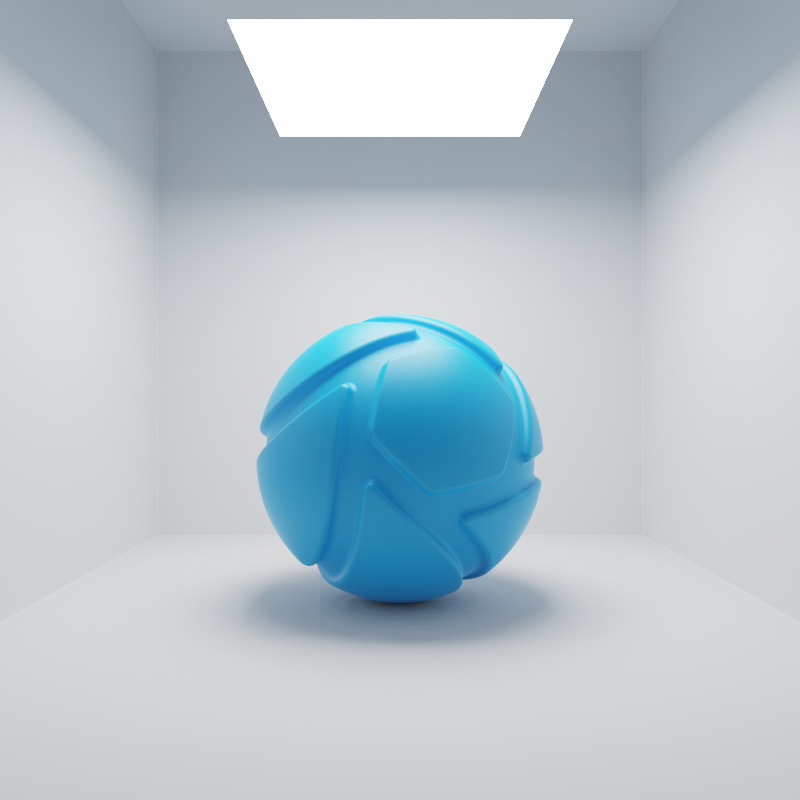


Lux
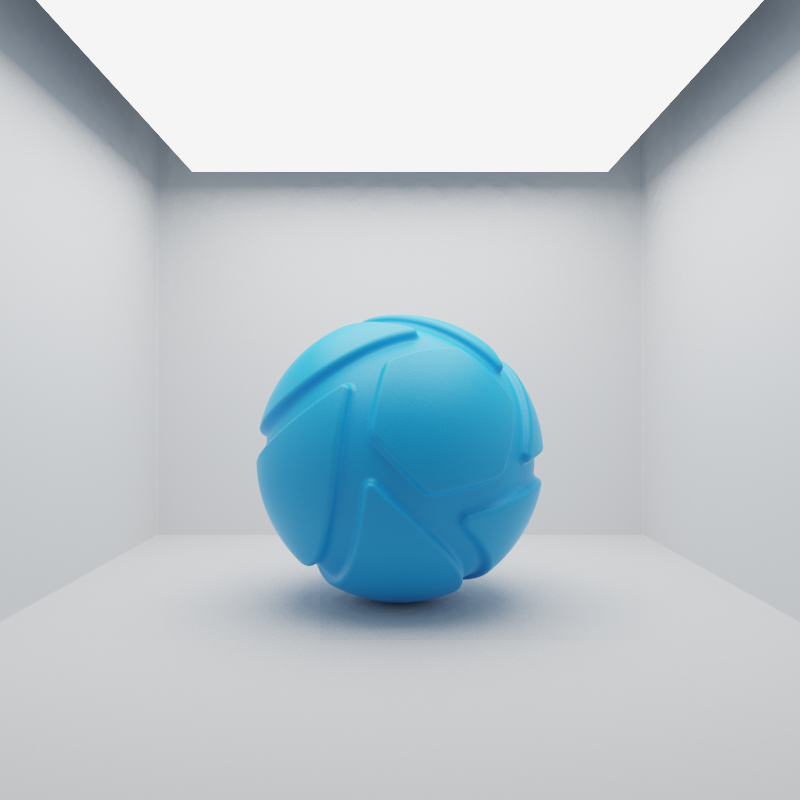
When the Power unit is set to Lux, then the light output is specified as luminous emittance. 1 Lux equals 1 Lumen per square meter of light-emitting surface. Total light output will vary for area light objects of different sizes. Small area lights are dim, while large area lights are brighter, since the light-emitting surface area is larger.
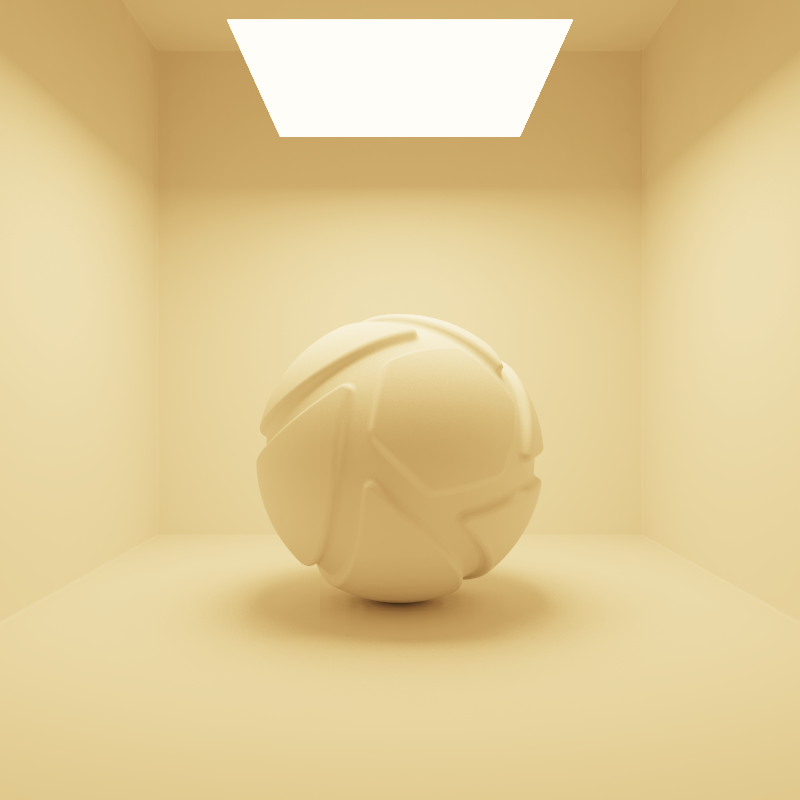
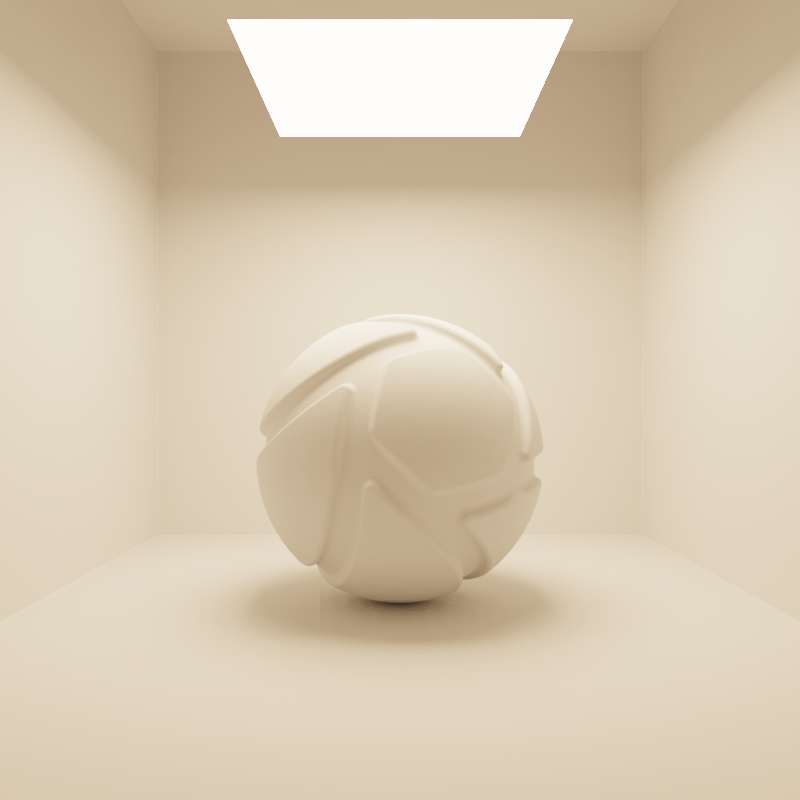
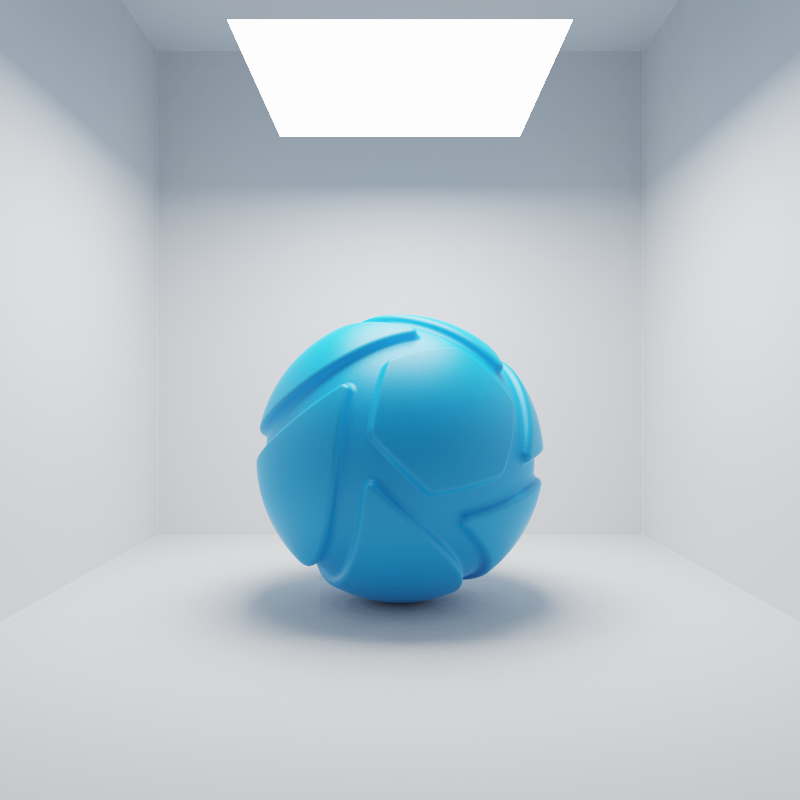
The examples below show the effect of increasing the size of a square area light from 10 to 200 mm. Power is a constant 25000 Lux.
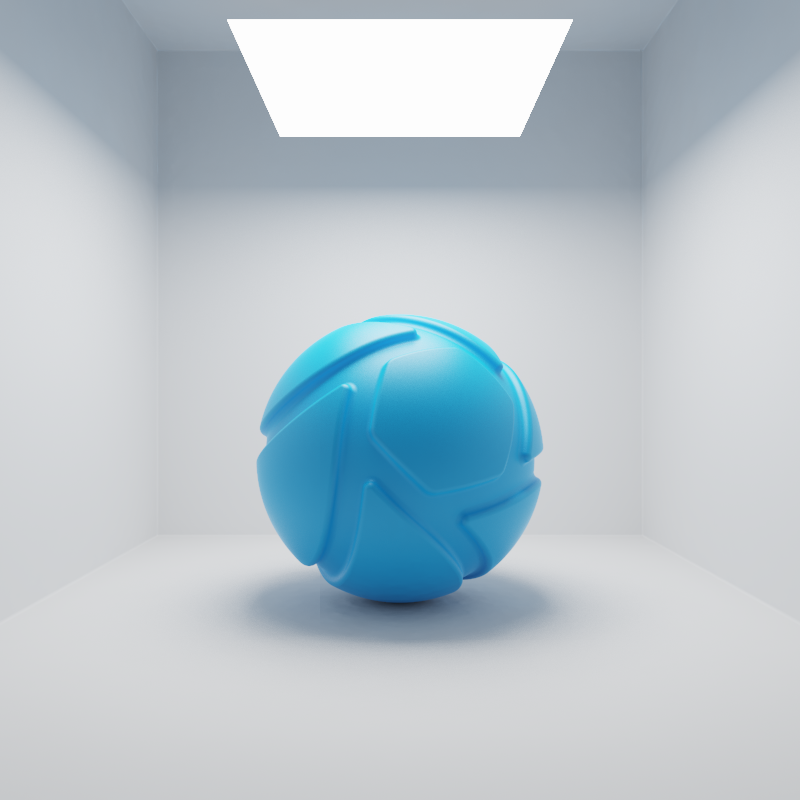


Tip
The softness of shadows from an area light is closely related to its size. A large area light produces soft shadows, while a small area light results in harder shadows with crisply defined, sharp edges.
Apply to Geometry
There are two checkboxes to make an area light emit from the front, back or both sides of the geometry. Which side of the geometry is interpreted as front or back depends on the orientation of the surface normals.
Toggling these options is most useful for surface geometry without thickness.
Apply to Front of Geometry
Apply to Back of Geometry

Apply to Front and Back of Geometry

Visible to Camera
Here, you can toggle whether or not the light source geometry is shown in real-time window and renderings.
The examples below show the effect of toggling visibility to camera.


Visible in Reflections
Here, you can toggle whether or not the reflection of the light source is shown in real-time window and renderings.
The examples below show the effect of toggling visibility in reflections.
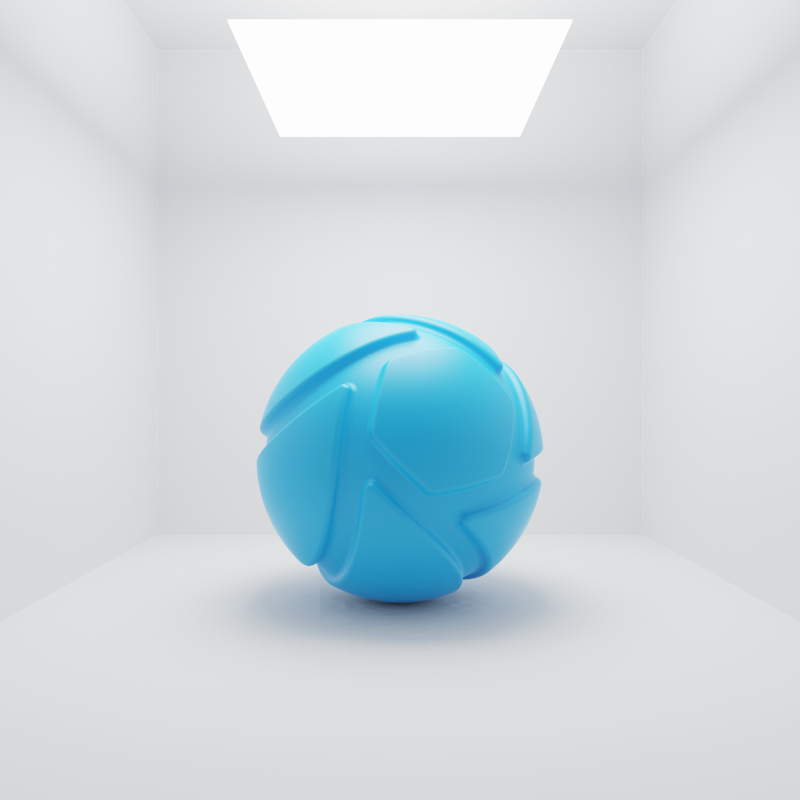
Reflections in Plastic material
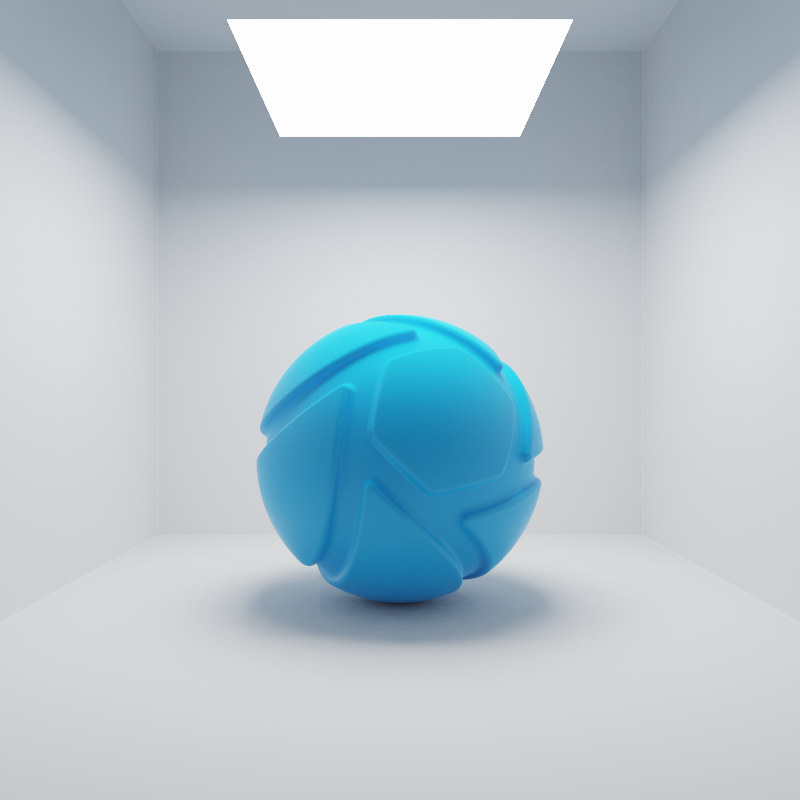


On the left the area light is visible in the reflections on the right the option is unchecked.
Reflections in Metal material
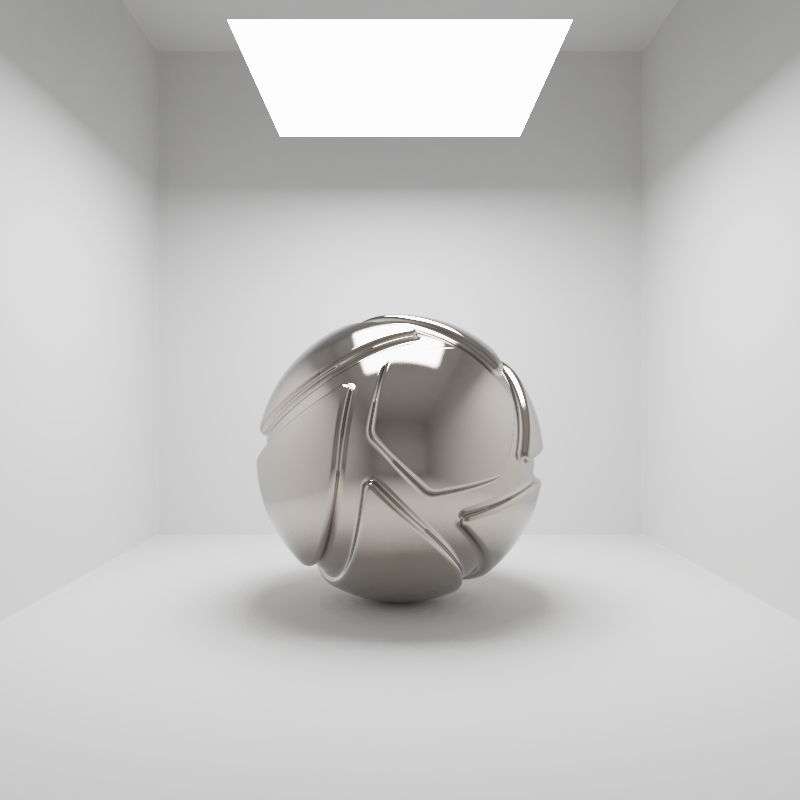
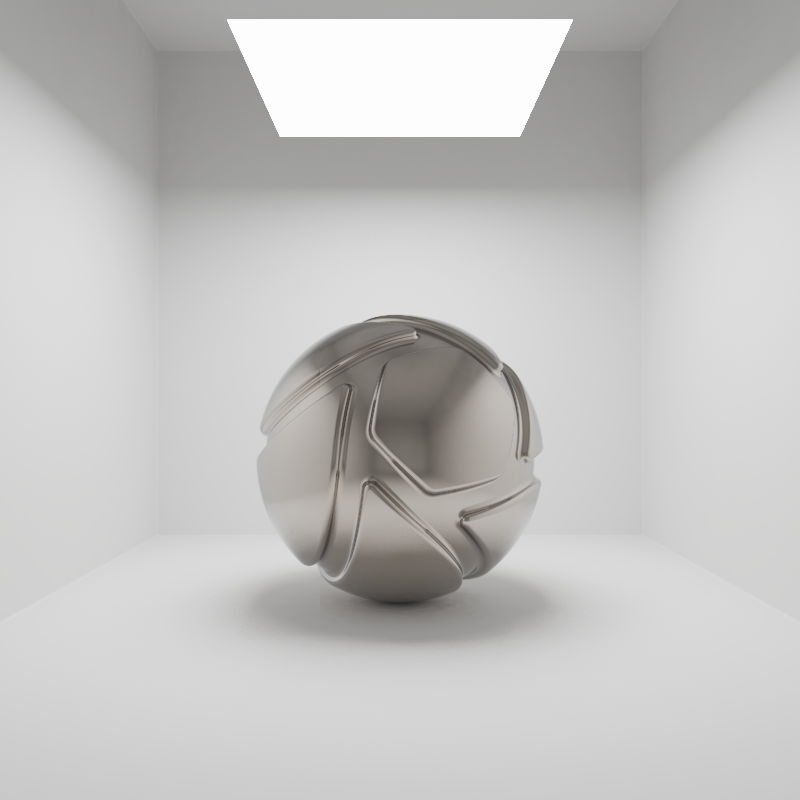


On the left the area light is visible in the reflections on the right the option is unchecked.
Visible in Shadows
Here, you can toggle whether or not the light source geometry casts a shadow in the real-time window. Disabling allows light to pass through the area light object. This option is disabled by default so as not to block any other light sources, including HDRI lighting.
The examples below show the effect of toggling visibility in shadows. The scene is lit by a large area light with a warm color (HSV: 30°, 90%, 100%) and a slightly smaller area light with a cool color (HSV: 225°, 35%, 100%) directly below it. Visible in Shadows is toggled for the smaller, cool area light.


With Visible in Shadows checked, the cool area light blocks the warm area light. As a result, the cool area light is the predominant light source in the scene, causing a clear blue cast.
With Visible in Shadows unchecked, light from the warm area light is able to pass through the cool area light. As a result, both area lights are contributing more or less equally to the scene’s lighting. The cool and warm light now blend, causing a warmer cast.
Samples
Use this slider to control the amount of samples used in the render.
Limitation
ZSpheres transferred from ZBrush are not yet supported as Area Lights.